-
Stable and Reliable integration of renewable energy
-
Support system with inertia problem avoiding frequency instability
-
Predictive maintenance on Components
Parallel processing enabled solution provides fastest approach for pre and post crises: No load shedding No oscillation, No Generation trip off.
-
With 90% reduction in switching losses
EcoPhi
Founded in 2023, EcoPhi is an academic spinout from Chalmers University based on 10 years of research.
What we do:
The opportunities are immense.
The opportunities are immense.
About Us
Empowering Renewable Futures with EcoPhi Technology




At EcoPhi, our mission is to revolutionize the renewable energy landscape by delivering advanced, AI-driven power electronics solutions. Our commitment is to foster a greener, more sustainable world by enabling efficient and stable integration of renewable energy sources.
As pioneers in the industry, EcoPhi specializes in creating high-capacity, GPU-based inverters and intelligent control systems designed for both residential and industrial applications. Our products stand out for their rapid response to energy fluctuations, unparalleled predictive maintenance capabilities, and innovative parallel processing technology, ensuring maximum efficiency and reliability.
Our team, composed of seasoned experts in renewable energy and AI technology, is dedicated to pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in energy management. By choosing EcoPhi, our clients not only invest in top-tier renewable energy solutions but also contribute to a greener planet.
EcoPhi’s approach goes beyond just supplying products; we are committed to building lasting relationships with our clients. From initial consultations to after-sales support, our focus is on delivering personalized service, clear communication, and comprehensive solutions that cater to the specific needs of each client.
Join us on our journey to power a brighter, more sustainable future with EcoPhi, where innovation meets environmental responsibility.

Research
EcoPhi foundation started 12 years ago at the university lab. They introduce a first use of Deep AI to electric power system sector by designing first AI driven grid forming inverters.
2015

Completing The First Project
The projects supported by Swedish Energy agency is completed in 2022 and several articles and publications has been published .
2022

EcoPhi Founding
Founded in 2023 as academic spinout from Chalmers University of technology.
2023

Example Title
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Mauris tempus nisl vitae magna pulvinar laoreet.
2005

Example Title
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Mauris tempus nisl vitae magna pulvinar laoreet.
2005
EcoPhi Driving Forces
The future of power grids starts here.

Many countries, including Sweden, Germany, Japan and India are establishing or have already implemented standards and norms pertaining to energy consumption and carbon footprint reduction. Efficient energy consumption is one of the most cost-effective methods for the reduction of carbon footprints and is therefore in line with EcoPhi's purpose.
The current modes of transmission and distribution of electricity are unreliable, unstable, and inefficient to meet customer demand owing to outdated or aging infrastructure. Hence, the aging energy
infrastructure needs to be either upgraded or replaced with smart grid technology to achieve high performance and minimize power outages over an extended period.
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources has propelled the need for smart grid
technology. With over 15% of energy now generated from renewables, smart grids offer reliability, resilience, and outage management capabilities. By leveraging cloud-based data processing and autonomous control, smart grids enable faster power restoration, reduce outage costs, and optimize renewable energy integration. In summary, smart grids transform traditional grids, providing enhanced reliability, cost savings, and a more sustainable energy
future.
Governments across the world have imposed several supportive policies and mandates, focusing on implementing smart grids and spreading awareness about energy conservation. These regulations drive the adoption of smart grid technology for industrial,
commercial, and residential applications.
Where do we add value?
1.
Grid Stability on provided from RES
Enables RES to not only provide energy but also contribute to stability
2.
Utilization of existing infrastructure and partnerships
Allows for smooth implementations and creates an advantageous position in the value chain.
3.
Predictive Maintenance on the RES and components nearby in grid
Our can sample environment with 1 million sample per second means that any small anomalies can be related to failure of components can be observed and predicted
4.
Reduces costs related to O&M
Related to interruptions, damaged equipment, components, etc.
Product Features
How it works - the technology process.
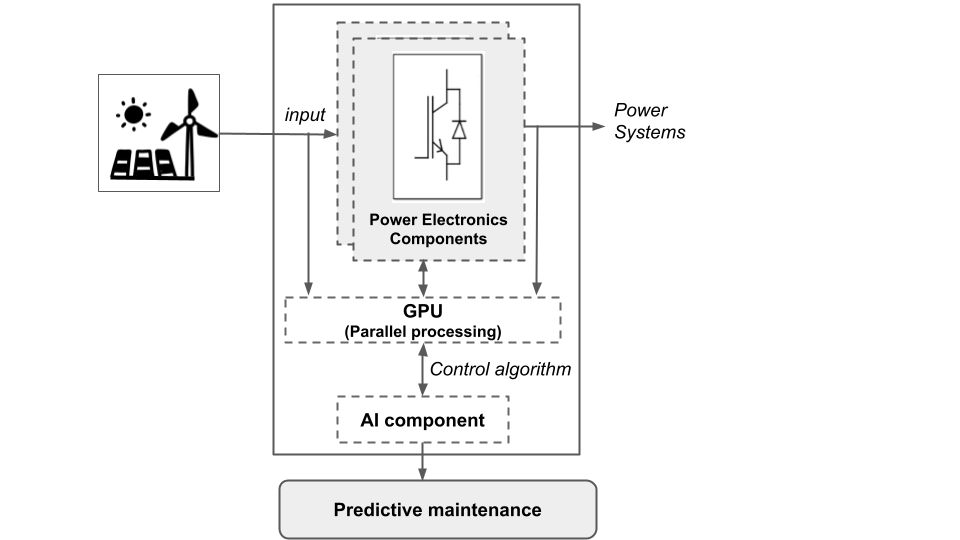

Analytics Platform
High-Frequency Sampling
EcoPhi’s system conducts high-resolution monitoring by measuring voltage and current at a rate of 1 million samples per second, which facilitates the early detection of component failures within renewable energy installations.
GPU-Accelerated Processing
The use of GPUs enables parallel signal processing, allowing for rapid analysis and response times, reducing the risk of power outages.
AI-Based Automatic Control
The product incorporates an artificial intelligence control system that autonomously reacts to fluctuations or crises in the energy system, ensuring operational stability.
Oscillation Control Post-Crisis:
EcoPhi’s AI engine is designed to mitigate post-crisis oscillations, maintaining the stability of power plants and preventing trips that could lead to wider power disruptions.
Meet the people in EcoPhi
Powering a Sustainable Future - The EcoPhi Team

Dr. Ebrahim Balouji
CEO & Founder
Dr. Ebrahim Balouji holds double Ph.D. s in Power Engineering, Machine Learning and AI. More than 12 years of experience in industry and academia.

Prof. Ozgul Salor
CTO
Ph.D. s Signal Processing More than 25 years of experience in industry and academia.

Dr. Karl Bäckström
Ph.D. in Computer Science
AI and Machine Learning Engineering With Industry Experience in Volvo and Ericsson